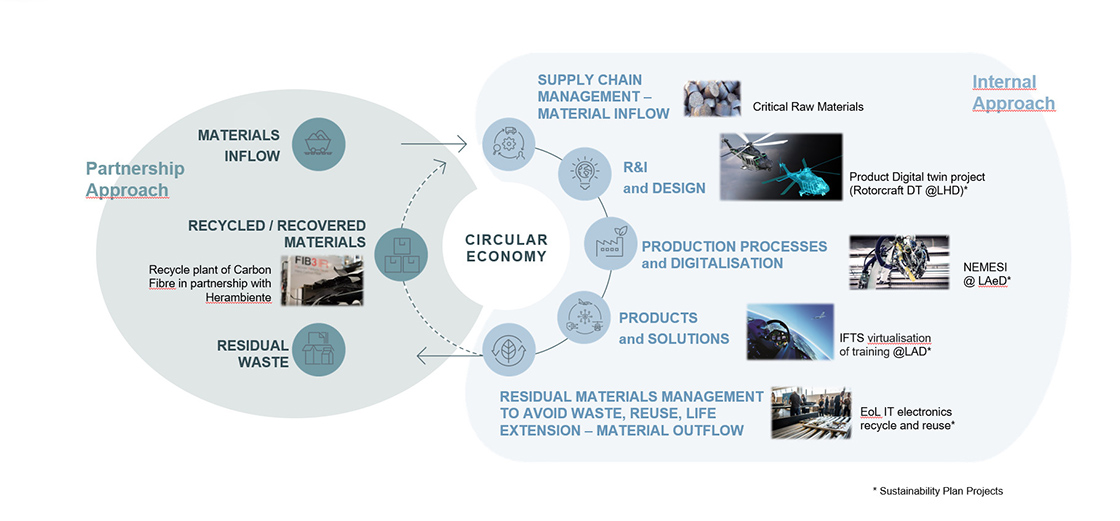
LEONARDO'S CLIMATE COMMITMENT
Leonardo, in line with major industry peers, is committed to strengthening its leadership in security and technology that can promote sustainability and climate action. The latter aims to avoid the effects of climate change and to be a lever to increase Leonardo's sustainable business proposition competitiveness. The Group is committed to reducing its greenhouse gas emissions throughout the value chain. Direct and indirect emissions (Scope 1 and 2) are lowered mainly through increased operations efficiency and energy efficiency initiatives.
The Group also works to reduce other emissions (Scope 3) by playing an active role in supporting suppliers' decarbonization roadmap and developing products with reduced impact on climate and ecosystems. As part of its climate strategy, Leonardo has defined three “near-term” emissions reduction targets, which have been validated by the Science Based Targets initiative (SBTi) in 2024. These targets, aligned with the Paris Agreements to limit global warming, reflect the company's tangible commitment to a transition to more sustainable operating and production models.
LEONARDO'S SBTi TARGETS AND DECARBONIZATION ROADMAP
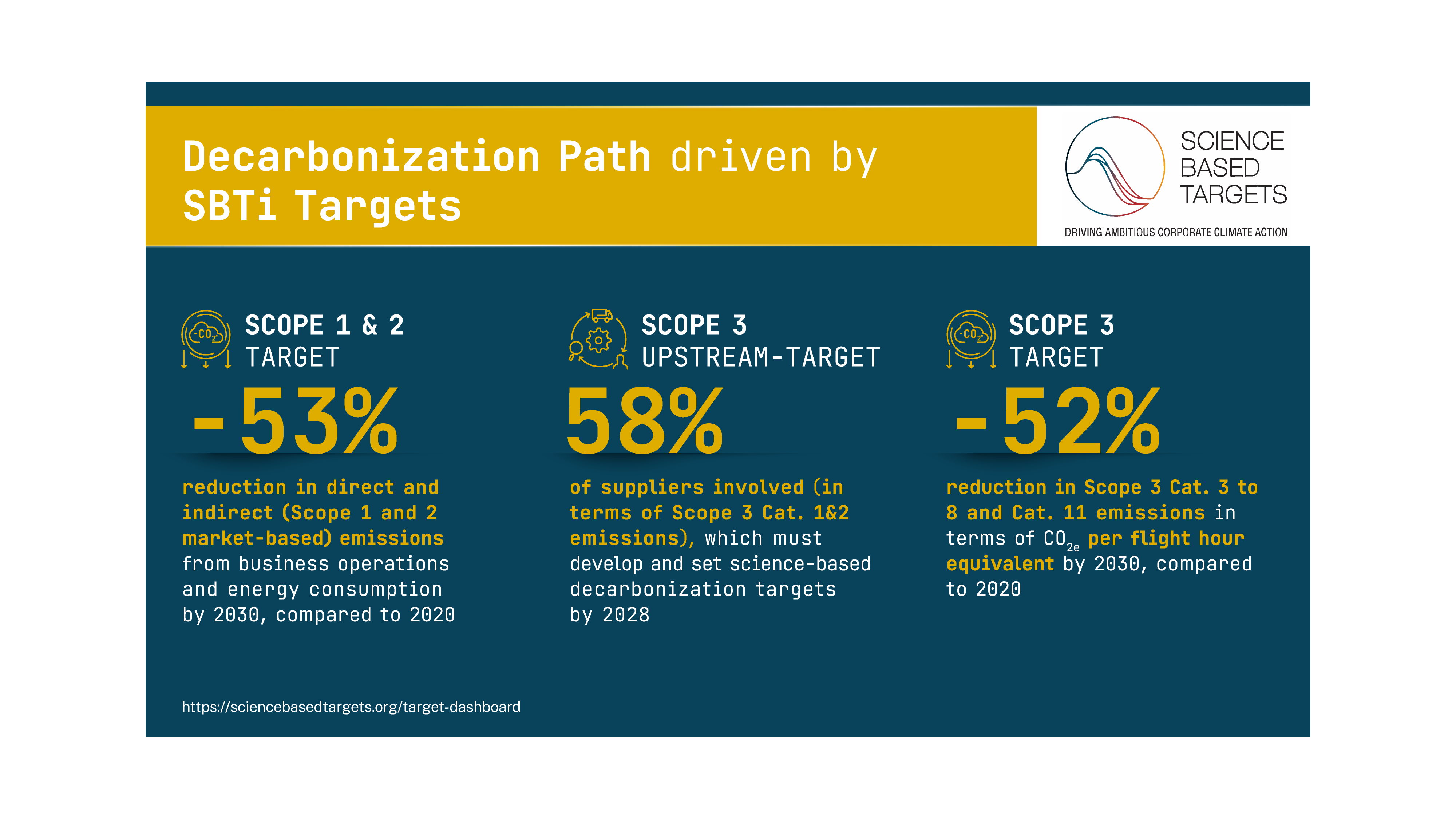 Target dashboard - Science Based Targets Initiative
Target dashboard - Science Based Targets Initiative
Leonardo tackles climate change with an integrated approach involving all emission categories (Scope 1, 2 and 3). The company is committed to improving energy efficiency in its operations, transforming production processes through lower environmental impact solutions and accelerating the adoption of renewable energy, a commitment that, over the past four years, has enabled the Group to achieve the following results:





 Energy efficiency
Energy efficiency Energy transformation plant and process efficiency
Energy transformation plant and process efficiency Energy mix rebalancing
Energy mix rebalancing Other projects
Other projects Virtualisation
Virtualisation  Reducing emissions during aircraft operation
Reducing emissions during aircraft operation Sustainable mobility of employees and shipping
Sustainable mobility of employees and shipping